Single Cycle Steam Turbine
When it comes to thermal engines and vapor power cycles, pressure and temperature or Enthalpy or simply the energy level which of the fluid ( working fluid ) entering into the engine is the one of most important factor on which engines are designed and efficiency with which energy is extracted.
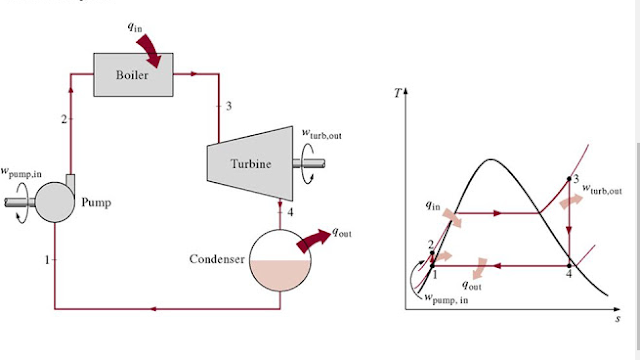
Steam turbine cycle is called Rankine Cycle which is the combination of thermal processes which made a thermal cycle completed and effective practically. Rankine Cycle Ideally contain four processes two of them add energy into a fluid and other two extract energy from other fluid.
The Processes are as follows:
- Isentropic expansion of steam in turbine( energy extraction for Electricity from Turbine ).
- Constant Pressure heat removal in condenser.
- Isentropic compression in a pump( famously known as Feedwater Pump)
- Constant Pressure heat addition in boiler.
This Cycle wasn't efficient enough to produce electricity, efforts after designing of blades, were done to increase its efficiency which include:
- Reheating
- Regeneration
- Super Critical cycle
Reheating
The Idea is to use the energy of the steam (at around 50 bar, 550 C) first at higher enthalpy , at first portion (High pressure turbine) and then this steam expands and give energy to turbine and this steam reaches at lower pressure( around 30 bar, 380 C ) and then here only option to increase the temperature which is done by reheating the steam in Super-heater of boiler and increase its temperature. Then this steam at IP portion(intermediate pressure turbine) same pressure but higher temperature ( with higher enthalpy as compared to at the end of HP turbine) enter into IP turbine.
Usually in higher capacity power plants, steam turbine with double reheating is being used, more than two reheat is theoretically won't be effective.
Double reheating is done by reheat the steam at the end of IP turbine in the super-heater and then the same process is done with now at lower pressure and temperature. Steam then enter into the last portion of turbine which called LP turbine( Low Pressure Turbine).
Regeneration
There is regeneration cycle which is called Stirling cycle, follows in Stirling Engine, whose ideal efficiency is same as Carnot Cycle and Ericsson Cycle, which are ideal cycle.
In power plant, regeneration cycle or regeneration is used to achieve the positive side of regeneration cycle along with reheating, co generation and super-critical cycle to increase overall efficiency.
This regeneration cycle is used by extracting high pressure and temperature steam from turbine intermediate stages to different other equipment(Auxiliaries of steam turbine cycle steam heater,ejector, deareator etc.). Air used for combustion of fuel is preheated and feed water is heated using steam etc.
Steam Turbine Thermal Efficiency is maximum to the date is 42 % .
There is regeneration cycle which is called Stirling cycle, follows in Stirling Engine, whose ideal efficiency is same as Carnot Cycle and Ericsson Cycle, which are ideal cycle.
In power plant, regeneration cycle or regeneration is used to achieve the positive side of regeneration cycle along with reheating, co generation and super-critical cycle to increase overall efficiency.
This regeneration cycle is used by extracting high pressure and temperature steam from turbine intermediate stages to different other equipment(Auxiliaries of steam turbine cycle steam heater,ejector, deareator etc.). Air used for combustion of fuel is preheated and feed water is heated using steam etc.
Steam Turbine Thermal Efficiency is maximum to the date is 42 % .


No comments:
Post a Comment